
Established in 1776, the United States developed a democracy that was influenced by the classical liberal thinkers of the day. It is also fair to say that the American approach to liberal democracy has been influential in its own right. The United States is an economic, military, and political superpower that has encouraged other nations to adopt its brand of liberalism, on occasion even imposing it on other nations. American cultural industries, with their global reach, have helped to shape not just the American concept of what a liberal democracy is, but the world’s view.
Given the influence that the United States has in the world, it is important then, to examine how liberal ideas have shaped the government of the U.S. and how ideals of liberalism have been implemented and modified in America.
In this lesson, you will explore the question: How has the United States interpreted liberal principles and integrated them into its governmental structure?

In the first two decades of the 20th century, a liberal movement called Progressivism became influential in the United States. Progressives like President Theodore Roosevelt and Robert La Follette sought to make changes to the existing economic and political order. Many progressives felt that, even though the United States was founded on the principles of liberalism, political power was still concentrated in the hands of too few people. Progressives successfully instituted several democratic reforms, especially at the state level of government. Some of these reforms included:
Like Canada, the United States generally uses the first-past-the-post system to determine which candidate becomes the people’s representative. However, U.S. politics is dominated by two political parties, the Republicans and the Democrats. While other parties and independent candidates may still run for election, they seldom capture a significant share of the vote. This means that candidates who get the most votes usually also have won the majority of votes cast and can justifiably claim to represent a majority of their constituents.
One area where the first-past-the-post system is not used in the U.S. is in the selection of the president. The president is selected using the electoral college system. Under this system, voters cast ballots for their choice of president, but the president is not directly elected based on that vote. Instead, each state is assigned several electors based on the number of representatives it has in the legislative branch of the federal government. These electors are the people who cast the votes that decide which presidential candidate will become the president. The electors, however, generally don’t get to decide how they vote. They are usually expected to cast their vote based on which candidate has won the popular vote in the presidential election in their state. Ultimately, it is expected that electors will exercise the will of the people.
The structure and workings of the federal government of the United States share many similarities with Canada, but there are some important differences.
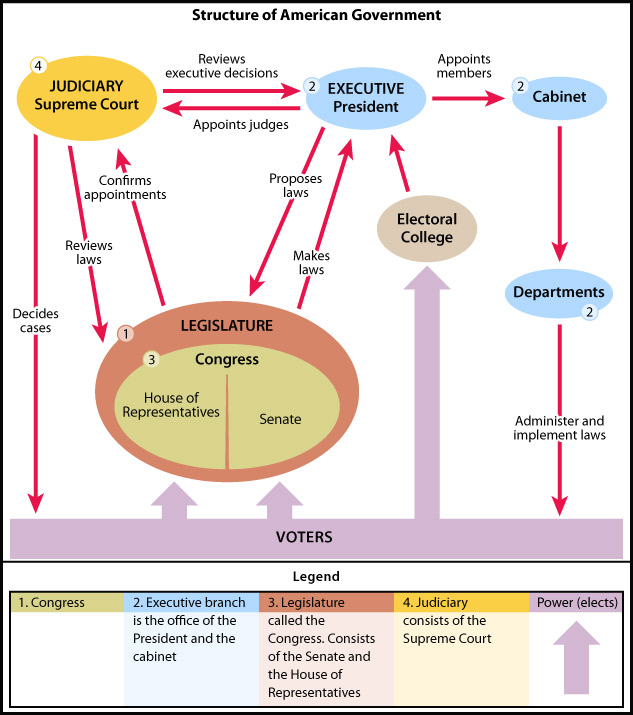
Watch this video explaining the Branches of the US Government:
In the United States, the Constitution is one written document—the Constitution of the United States of America. In Canada, the constitution is a combination of a written document and laws and traditions that are established “conventions” that are said to have a “constitutional effect.”
Constitution: a system of laws that formally states people's rights and duties
Popular vote: the percentage of the total votes cast received by a candidate or a political party
Progressivism: a liberal movement of the early 20th century that sought political, economic, and social reform in the United States.
Residual powers: ensures that every area of legislation comes under one or both orders of government
Secret ballot: the provision that voters should be able to cast their ballot in private and that no other individual should know how they voted unless the voter wishes to inform them.
The United States is seen by many as one of the great liberal democracies of the modern world. While its governmental structure and constitution were influenced by the ideas of early liberal thinkers, many segments of American society were excluded from the rights and protections built into the constitution. The concept of liberalism in the United States continued to evolve. That evolution can be traced to the amendments to the U.S. Constitution.
Like many nations, the United States continues to struggle with the idea of how liberal a liberal democracy should be. The information and concepts you have explored in this lesson will serve as a good foundation as you begin to look at this issue yourself later in the course.
You have explored liberalism as it has evolved within the democracies of Canada and the United States. Although on different timelines and to different degrees the governments of both nations have gradually broadened suffrage and expanded the notion of basic rights.
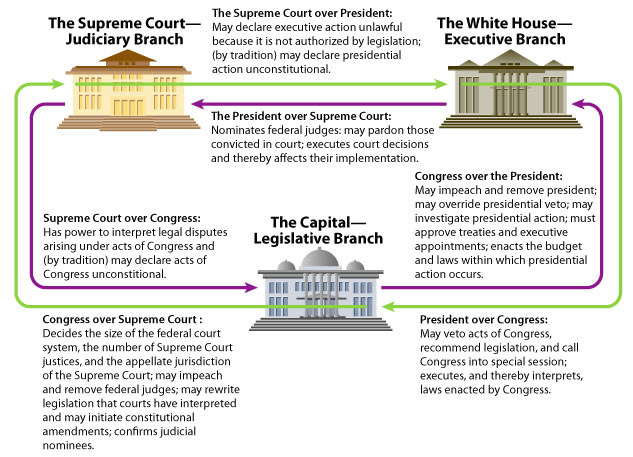
The two nations have embarked on slightly different courses in their approach to the structure of government. Canada’s parliamentary system fuses the role of the executive branch with the legislative branch and relies on the principle of responsible government to check the power of the executive. The United States, on the other hand, has solidly embraced the concept of separation of powers and has built in a series of checks and balances to ensure that no branch of government can entirely dominate the others. Despite these differences, both systems incorporate basic principles of liberalism such as government accountability to the people and constitutional protection of individual rights.
The different approaches taken to choosing and structuring government each have their strengths and weaknesses. Having assessed many of those strengths and weaknesses you will be better equipped to tackle the key inquiry for this unit:
To what extent are the modifications made to liberalism in the 20th and 21st centuries justifiable?
Using the Internet, research the Constitution of the United States of America and consider: