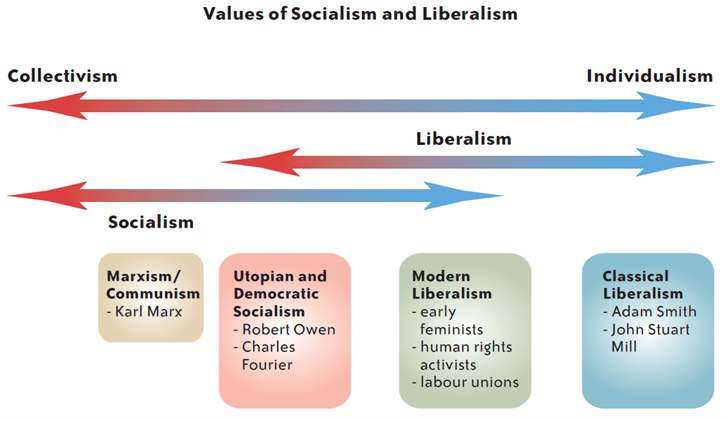
By now in your life, you have undoubtedly encountered the words “liberal” and “liberalism” and started to develop your own picture of what the words mean. In this unit you will look deeper into the meanings of those words, building on your prior knowledge and clarifying and modifying your understanding of liberalism.
You will also begin a journey into the past. The English word “history” is derived from the ancient Greek word historia, which means “finding out” or “to learn by investigation or inquiry”. In order to improve your understanding of the modern view of liberalism this unit will require you to “find out” about the early history of liberalism. You will learn about the cultures and societies that pioneered many of the principles of liberalism in the distant past. You will familiarize yourself with the concept of liberalism that developed in Western Europe and America during the 18th and 19th centuries and you will discover how these theories were put into practice. Finally, you will begin to evaluate 18th and 19th-century liberalism, identifying the successes and failures that resulted from the practical application of liberal ideology.
On completion of the unit, you should be well-positioned to respond to the key question explored in the unit, “How did liberalism originate?”
As you become more aware of the positive and negative societal impacts that can take place when theories and ideas become policies and practices, you will be closer to deciding to what extent we should embrace an ideology like liberalism, and what kind of liberalism.
As a citizen, you have a stake in how governments react to the political and economic challenges before them. This unit will help you understand how liberalism has evolved over the past 130 years. This unit will also help you provide informed input into how you think liberalism should evolve in the future.

In this unit, students will explore the following questions.
To cover the outcomes, there will be 15 main lessons.
| Lesson | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ideological perspectives Under Liberalism |
| 2 | Exploring the Political Spectrum |
| 3 | Early Origins of Liberalism |
| 4 | The Enlightenment and Philosophers |
| 5 | The Development of Classical Liberalism |
| 6 | Life Under Classical Liberalism |
| 7 | Evolution of Modern Liberalism |
| 8 | John Stewart Mill |
| 9 | Classical Becomes Modern |
| 10 | Political Liberalism and the Canadian Government |
| 11 | Political Liberalism and the United States Government |
| 12 | What is an Economic System |
| 13 | The Markey Economy and Liberal Ideology |
| 14 | The Mixed Economy and Liberal Ideology |
| 15 | Two Economic Approaches |
Graded work includes three discussions, a unit quiz, and an assignment. Graded work will appear on its own content page so you can clearly identify what to turn in and where. Due dates can be found in the course Checklist. If ever you cannot meet a course due date, let your teacher know through private discussions.
The vocabulary below will used and covered in this unit.